How does the eye work? Understanding vision and why eye protection matters
The human eye is one of the most sophisticated sensory organs in the body. It constantly captures light, adjusts focus, and sends visual information to the brain, all in a fraction of a second. This remarkable process enables us to navigate complex environments, detect hazards, and perform precise tasks.
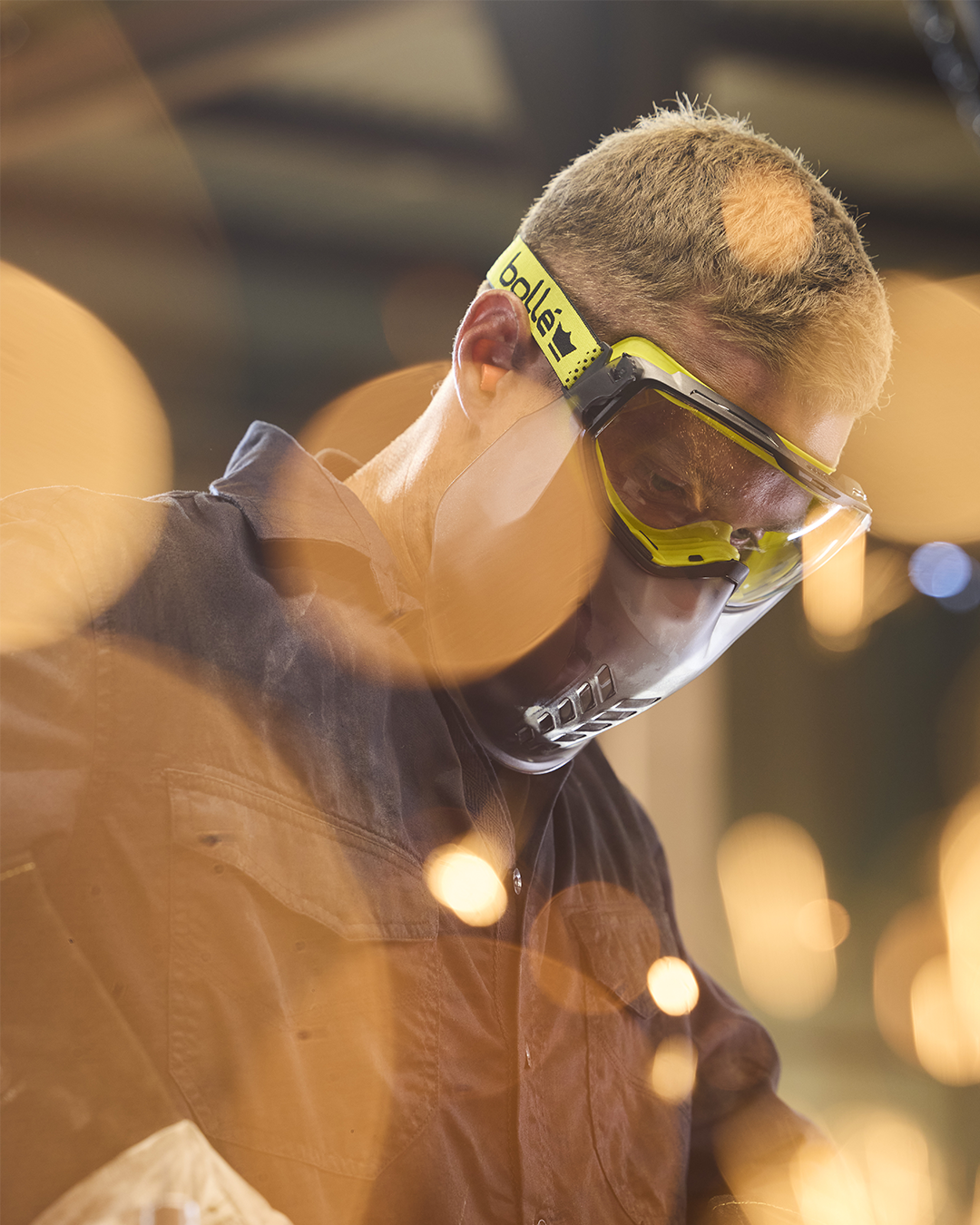
At Bollé Safety, we know that understanding how vision works is essential to protecting it effectively. Despite its complexity, the eye is also fragile, making it highly vulnerable to injury without proper protection.
How the eye works: The basics of vision
The eye functions in a coordinated sequence, similar to a high-performance
camera:
-
Light enters through the cornea, the eye’s clear outer surface.
-
The lens adjusts to focus light at different distances.
-
The retina converts light into electrical signals.
-
The optic nerve transmits these signals to the brain.
-
The brain interprets the information as the images we see.
Even small disruptions like dust, impact, or glare can interfere with this process and affect how we perceive the world.
Why the eye is so vulnerable
The structures of the eye, including the cornea, lens, retina, and optic nerve, can be damaged through:
-
Mechanical impact
-
Flying debris
-
Chemical splashes
-
UV radiation
-
Digital screen glare
Eye injuries can range from minor irritation to severe trauma and permanent vision loss. Because the eye has limited capacity for self-repair, preventing injury with protective eyewear is essential.
Shocking workplace eye injury statistics (US and more)
Work-related eye injuries remain a significant safety issue around the world:
- In 2020, there were 18,510 eye-related injury and illness cases in U.S. workplaces that resulted in at least one day away from work, an incidence rate of 1.7 cases per 10,000 full-time workers. source
- According to the International Labour Organization and International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness, approximately 3.5 million eye injuries occur in workplaces worldwide every year, representing about 1% of all non-fatal occupational injuries. source
- Globally, over 13 million people live with vision impairment linked to their work. source
- Nearly 20,000 eye injuries occur annually in the United States alone, often requiring one or more missed work days, and many result in serious trauma or long-term vision issues. source
These statistics highlight not only how common eye injuries are, but how preventable most of them would be with proper protection and compliance.
The true cost of eye injuries
Eye injuries have costs beyond personal pain and impairment:
-
Medical treatment
-
Workers’ compensation
-
Lost productivity
-
Missed work time
For example, estimated workplace eye injuries in the U.S. can cost employers and insurers hundreds of millions of dollars annually.
Eye protection is proven prevention
Most serious eye injuries are preventable with the right protective eyewear. Safety professionals and health organizations agree that:
- Proper eye protection can reduce the severity or prevent up to 90% of eye injuries when worn correctly.
Yet, many workers either do not wear eye protection, or wear the wrong type, exposing themselves to avoidable risk.
Designing eye protection that people love to wear
To be effective, protective eyewear must do more than block hazards : it must also support natural vision. High-quality eye protection should:
-
Maintain clear optical performance
-
Protect against impact, dust, and chemical exposure
-
Filter harmful UV and blue light
-
Prevent fogging (anti-fog lenses)
-
Be comfortable enough to wear consistently
Discover our decision guide to help choose the right protection :
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about vision and eye protection
How does the human eye work?
The eye works by capturing light through the cornea, focusing it with the lens onto the retina, and converting it into electrical signals. These signals travel through the optic nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as images.
Why is the eye sensitive to injury?
The eye contains delicate structures such as the cornea and retina that cannot regenerate easily. Even minor trauma, chemical exposure, or radiation can cause lasting or permanent vision damage.
What are the most common causes of eye injuries at work?
Common causes include flying particles, dust, chemical splashes, impact, UV radiation, and improper use of tools or machinery. Many injuries occur when eye protection is not worn or is not suitable for the task.
Can eye injuries be prevented?
Yes. According to occupational health organizations (source higher up), up to 90% of workplace eye injuries can be prevented with proper protective eyewear that is correctly selected and worn.
Why is eye protection important even for short tasks?
Many eye injuries happen in seconds and during routine tasks. Short exposure to hazards such as debris, chemicals, or intense light can cause serious injury without warning.
What types of eye protection are used in professional environments?
Depending on the risk, eye protection may include safety glasses, goggles, face shields, or filter lenses designed to protect against impact, dust, chemicals, radiation, or glare.
How does blue light affect vision?
Prolonged exposure to blue light from digital screens can contribute to eye strain, visual fatigue, and discomfort. Lenses designed to filter blue light can help reduce these effects during screen-intensive work.
Is eye protection a legal requirement at work?
In many countries, employers are legally required to assess risks and provide appropriate personal protective equipment, including eye protection, when hazards cannot be eliminated.
Why is comfort important in protective eyewear?
Protective eyewear must be comfortable to ensure it is worn consistently. Poor fit, fogging, or optical distortion often lead to non-compliance, increasing the risk of injury.
How does understanding vision help improve eye protection?
Understanding how the eye focuses, adapts to light, and processes information allows protective eyewear to be designed in a way that preserves visual clarity while maximizing safety.